Boost Manufacturing Efficiency With Odoo MRP and PLM
In the modern industrial world, companies face increasing challenges in ensuring that they make the most of their resources and achieve competitive differentiation. In this article, we will highlight ERP for Manufacturing Apps: Odoo's material requirements planning (MRP), and Product Lifecycle Management (MPL) software as essential tools for improving production processes and effectively achieving company goals.
Manufacturing resource planning (MRP) is an important system for streamlining production processes and optimizing resource utilization in manufacturing industries. By leveraging data on sales forecasts, inventory levels, and production capabilities, MRP creates material requirements and production schedules to ensure efficient production operations. This blog summary highlights the importance of MRP in reducing inventory costs, reducing lead times, and improving overall efficiency in manufacturing operations. Let us explore the prominent importance of MRP in the industrial environment.
What is the MRP Manufacturing Resource Planning System?
A manufacturing resource planning (MRP) systems consists of several components that work together to achieve production goals and manage resources effectively. Here are the most important components that form an essential part of an MRP system :
ERP master plan
An ERP master plan serves as a guiding roadmap, assisting in the alignment of ERP endeavors with business objectives. It enables meticulous long-term planning and assessment of business process requirements and priorities before allocating valuable time and resources.
- Strategize for the execution of enhancements
- Maintain oversight of expenditures
- Mitigate the risks of failures & interruptions to your business
BOM Management
BOM Management in MRP refers to the process of creating, organizing, and maintaining Bills of Materials (BOMs) within the Material Requirements Planning (MRP) module of the ERP system. This functionality allows users to define the components, raw materials, and sub-assemblies required to manufacture a finished product.
Master Production Schedule
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) in Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a dynamic plan that outlines the production quantities and timing for finished products over a specified time horizon. It serves as a crucial link between sales forecasts, production capacity, and inventory levels. The MPS takes into account factors such as customer demand, available production capacity, lead times, and inventory policies to generate a detailed schedule for production activities.
Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) refer to the quantities of raw materials, components, and parts needed to fulfill production orders or meet demand for finished products within a specified timeframe. MRP calculates these requirements based on factors such as the production schedule, bill of materials (BOM), lead times, and inventory levels.
Inventory System in MRP
The Inventory System in Material Requirements Planning (MRP) refers to the methodical management of inventory levels and stock movements within the context of the MRP process. It involves tracking and controlling the quantities of raw materials, components, work-in-progress, and finished goods to ensure optimal inventory levels are maintained to support production and meet customer demand.
Demand Planning
It involves forecasting and managing the expected demand for products or materials within a specified timeframe. It aims to predict future customer demand accurately to ensure that adequate inventory levels are maintained to meet customer needs while minimizing excess inventory and stock outs.
Capacity Planning
The process of Capacity Planning in MRP typically begins with evaluating the available capacity of each production resource, taking into account factors such as machine capacities, labor availability, shift schedules, and maintenance downtime. Based on this assessment, capacity requirements are compared with capacity constraints to identify potential mismatches or areas of underutilization.
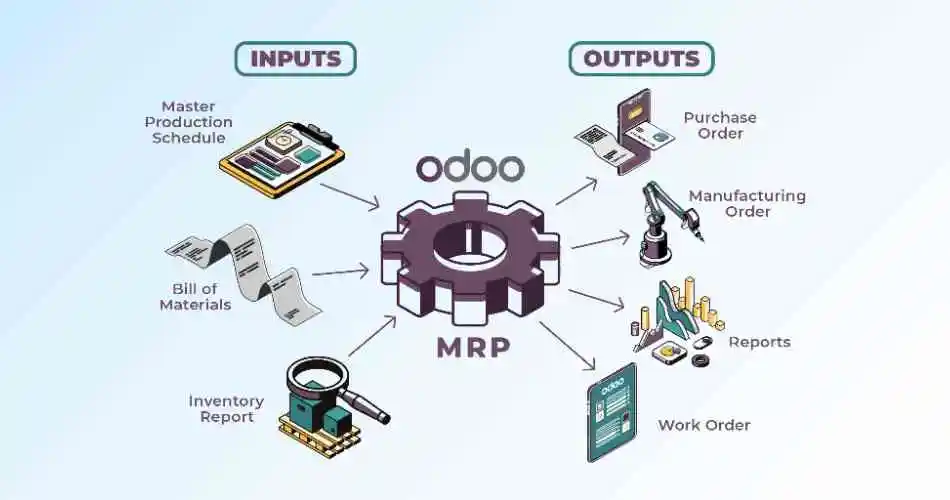
Importance of Improving Productivity and Achieving Manufacturing Excellence!
Manufacturing resource planning (MRP) system is a system used to manage and plan production operations in manufacturing companies. It aims to optimize resource utilization and accurately identify material needs, allowing companies to fulfill orders effectively and reduce costs.
Here are some reasons why a manufacturing chain program is especially important:
Improve planning and organization
MRP software helps improve production planning and organization processes, as it allows material and resource needs to be accurately determined based on expected demand and production schedule. By providing accurate estimates of needs and resources, MRP can reduce costs resulting from storing excess inventory and reduce loss and waste. Which will improve the response time for new requests and submit them in a timely manner.
Increase productivity, efficiency and improve product quality:
MRP software facilitates the planning of production processes and determining the optimal order for operating machines and using labor, which increases productivity and efficiency. By providing accurate traceability of materials and processes, MRP can improve the quality of products and ensure that quality requirements and standards are met. Thanks to the availability of shared central information, communication and cooperation between various departments within a company can be enhanced, facilitating coordination between production, supply, sales and finance.
In short, manufacturing chain software is a vital tool for manufacturing companies to improve planning, production, costs, quality and communication, helping them make the most of available resources and achieve competitive differentiation in the market.

Return On Investment In Implementing MRP System.
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, staying ahead of the competition requires more than efficient production processes – it requires strategic investments that deliver tangible results. One such investment that has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing operations is manufacturing resource planning (MRP). In this blog, we will delve into the significant ROI that businesses can achieve by investing in MRP
The formula for calculating ROI is as follows: (Total Investment Value - Total Cost of Ownership) / Total Cost of Ownership) x 100.
Let's take the example of a consumer goods (retail) manufacturer that has decided to invest in an ERP system. The company needs to calculate the ROI for its new solution three years after startup, based on an upfront implementation cost of SAR 50,000 and an annual maintenance fee of SAR 50,000. This results in a three-year bonus total cloud ownership cost of SAR 150,000. Of course, to simplify this example to fit this article; The total cost to the manufacturer may also include the cost of training employees to use the new ERP solution, implementation partner fees, etc., as well as pre-installation fees and annual license fees, depending on the specific use case and ERP deployment model. As for revenues, the manufacturer chose to focus on hard costs, so it calculated the increased sales growth, higher margins and lower production costs that could be attributed to its ERP system, as shown in this table:
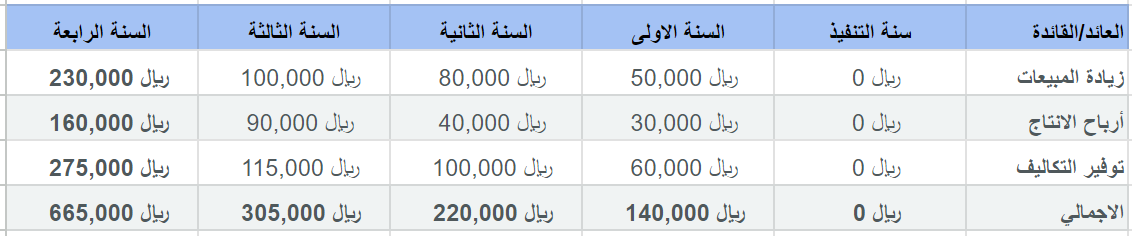
As we note, the value provided by the program during this three-year period is 665,000 riyals.
Adding the total value of the gains attributable to the ERP system and the simplified total cost to the manufacturer in the ERP ROI formula, we get:
(665,000 SAR - 350,000 SAR) / 350,000 x 100, which equates to a return on investment of 90%.
It is important to emphasize that the gains in this example are also simplified. The overall value a company can attribute to an ERP system depends on the nature of the business and may include improvements in product carrying, transportation, or inventory costs, increased order sizes, reduced headcount, and reduced administrative costs. In addition to these hard returns, a company may also derive intangible benefits from implementing an ERP system, such as improved employee morale, which should also be factored into ROI calculations.
Understand the difference between PLM and MRP
In the world of manufacturing and product development, two important systems play key roles in streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency: product lifecycle management (PLM) and manufacturing resource planning (MRP). While both systems are essential components of modern manufacturing operations, they serve different purposes and address distinct aspects of the product development and production process. Let us delve into the differences between PLM and MRP:
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM):
PLM is a comprehensive system that focuses on managing the entire life cycle of a product, from its conception and design to manufacturing, distribution, and even disposal. It includes a wide range of functions and processes, including product design and engineering, document management, collaboration, version control, and change management. Lifecycle management (PLM) aims to ensure that all stakeholders have access to accurate and up-to-date information about a product throughout its life cycle, facilitating effective collaboration and decision-making.
Main features of PLM:
- Product data management
- Document management and version control
- Collaboration tools
- the management of change
- Regulatory compliance management
- Quality Management
Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP):
A system that focuses primarily on improving production processes and managing physical resources. It helps manufacturers plan and control production activities, ensuring materials are available when needed and production schedules are met. MRP uses data about sales forecasts, inventory levels, and production capacity to create material requirements and production schedules, helping companies reduce inventory costs, reduce lead times, and improve overall efficiency.
Key Features of MRP:
- Material requirements planning
- Production scheduling
- Inventory Management
- purchase management
- The ability to plan
- Shop floor monitoring
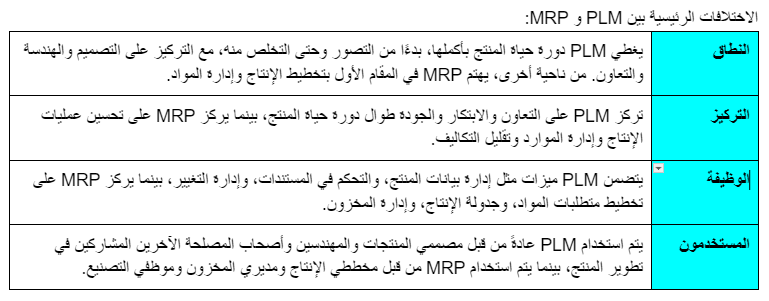
Key differences between PLM and MRP:
In summary, while both PLM and MRP are fundamental systems for modern manufacturing operations, they serve different purposes that address different aspects of the product development and production process. PLM focuses on managing the full life cycle of a product and facilitating collaboration and innovation, while MRP focuses on optimizing production processes and managing physical resources to ensure efficient production processes. By understanding the differences between PLM and MRP, companies can choose the right system or combination of systems to meet their specific needs and achieve their business goals.
In conclusion, investing in manufacturing resource planning (MRP) is not just a wise business decision – it is a strategic necessity for companies aiming to thrive in today's competitive manufacturing landscape. By streamlining operations, reducing inventory costs, accelerating time to market, enhancing decision-making, and ensuring compliance, MRP delivers a compelling return on investment that extends beyond financial metrics. It enables companies to achieve maximum efficiency, optimize resources, and seize growth and innovation opportunities, ultimately propelling them towards sustainable success and profitability.